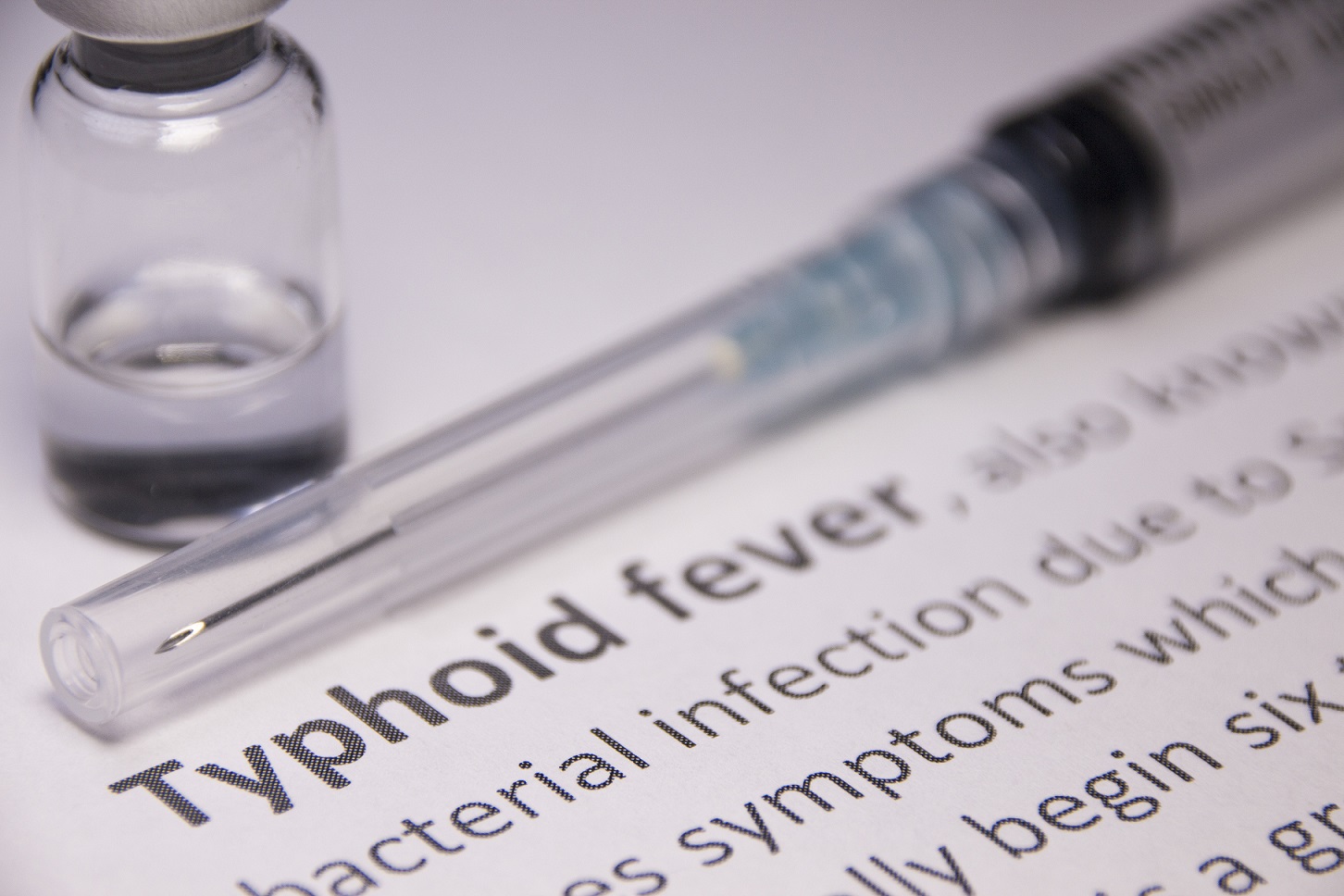
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that infants and children can be given a new typhoid conjugate vaccine when it is released in 2019. After collecting five years of follow-up observation data for seroconversion, WHO officials put forward recommendations to introduce the first typhoid conjugate vaccine for infants and children over six months of age as a single dose. The Typbar-TCV vaccine, under development by Bharat Biotech International Limited since 2001, was first licensed in India in 2013.1
The recommendations follow an evidence review by the WHO’s Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization2 in October 2017.
As a result of the WHO prequalification achieved in December of 2017, developing countries can apply for funding from Gavi, the Global Alliance for Vaccines & Immunization, which approved $85 million in funding for 2019-20 for the new typhoid vaccine’s introduction.3 The vaccine is expected to be fully released in mid-2019.
Typhoid fever is a water-borne bacterial illness, caused by Salmonella entericaserotype typhi and spread through contaminated food and water. It causes a high fever, gastrointestinal pain, loss of appetite, headaches and rashes. In severe cases, jaundice, bowel perforation and death can occur. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), typhoid can last from three to four weeks without therapies such as fluoroquinolone or other types of antibiotics. There has been an increase in the number of antibiotic-resistant illnesses,4 resulting in the use of antibiotics such as ceftriaxone and azithromycin. Each year, there are an estimated 12-20 million cases and 128,000-160,000 associated deaths from typhoid fever.5
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation-funded Typhoid Vaccine Acceleration Consortium (TyVAC) clinical trial6 focused on the vaccine’s cost effectiveness and efficacy began in February in Malawi. It includes 24,000 children aged nine months to 12 years. The study is in partnership with the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s Center for Vaccine Development, the University of Oxford’s Oxford Vaccine Group and international nonprofit PATH.
References:
1 Sabin Vaccine Institute. WHO recommends use of first typhoid conjugate vaccine. Sabin Vaccine Institute (press release) Apr. 3, 2018.
2 World Health Organization. Weekly epidemiological record. World Health Organization No 48, 2017, 92, 729–748 Dec. 1, 2017.
3 Gavi, The Vaccine Alliance. Millions of children set to be protected against typhoid fever. Gavi, The Vaccine Alliance (press release) Nov. 30, 2017.
4 First Typhoid Conjugate Vaccine Recommended by WHO. Contagion Apr. 3, 2018.
5 WHO. Typhoid Fact Sheet. WHO.int January 2018.
6 First child vaccinated with typhoid conjugate vaccine in Africa. University of Liverpool Feb. 21, 2018









2 Responses
This isn’t much of an article…..dry reporting. Provokes many questions that the author is unaware of?
Typhoid vaccine is very important of given for the each and every children at present. The good infants and protection is very important. The observation and official recommendations are given for governments for given this vaccine. The Typbar-TCV vaccine is developed under 2001 by BBIL. The funding and alliance are very important. Evidence and proof to be given for the government authority of given vaccine. The gastrointestinal and perforations is occur.So this is important for all children